The technology behind the heat exchangers makes them an excellent alternative both in heating systems and industrial refrigeration, replacing coils or other more basic equipment.

Although there are different uses for each type of existing heat exchangers, in general these equipment are used to recover heat between two currents that take part in a process. The efficiency of the entire system will depend on its proper choice, and of course, the saving of resources and increase in production.
What differentiates a plate heat exchanger (PHE)?
The plate exchangers belong to the subcategory known as indirect exchangers and they are those that use a flat wall as the separation surface between the fluids.
What are the advantages of this type of heat exchangers?
Although they are relatively recent, plate heat exchangers are displacing common or traditional heat exchangers because of the advantages they offer. Among them, its specialized design stands out, very suitable for transferring heat between medium and low pressure fluids.
Welded and semi-welded heat exchangers are used for the exchange of heat between high-pressure fluids or when a more compact product is required: instead of a pipe that passes through a chamber, they are composed of two alternate chambers, generally thin in depth, separated on its larger surface by a corrugated metal plate.
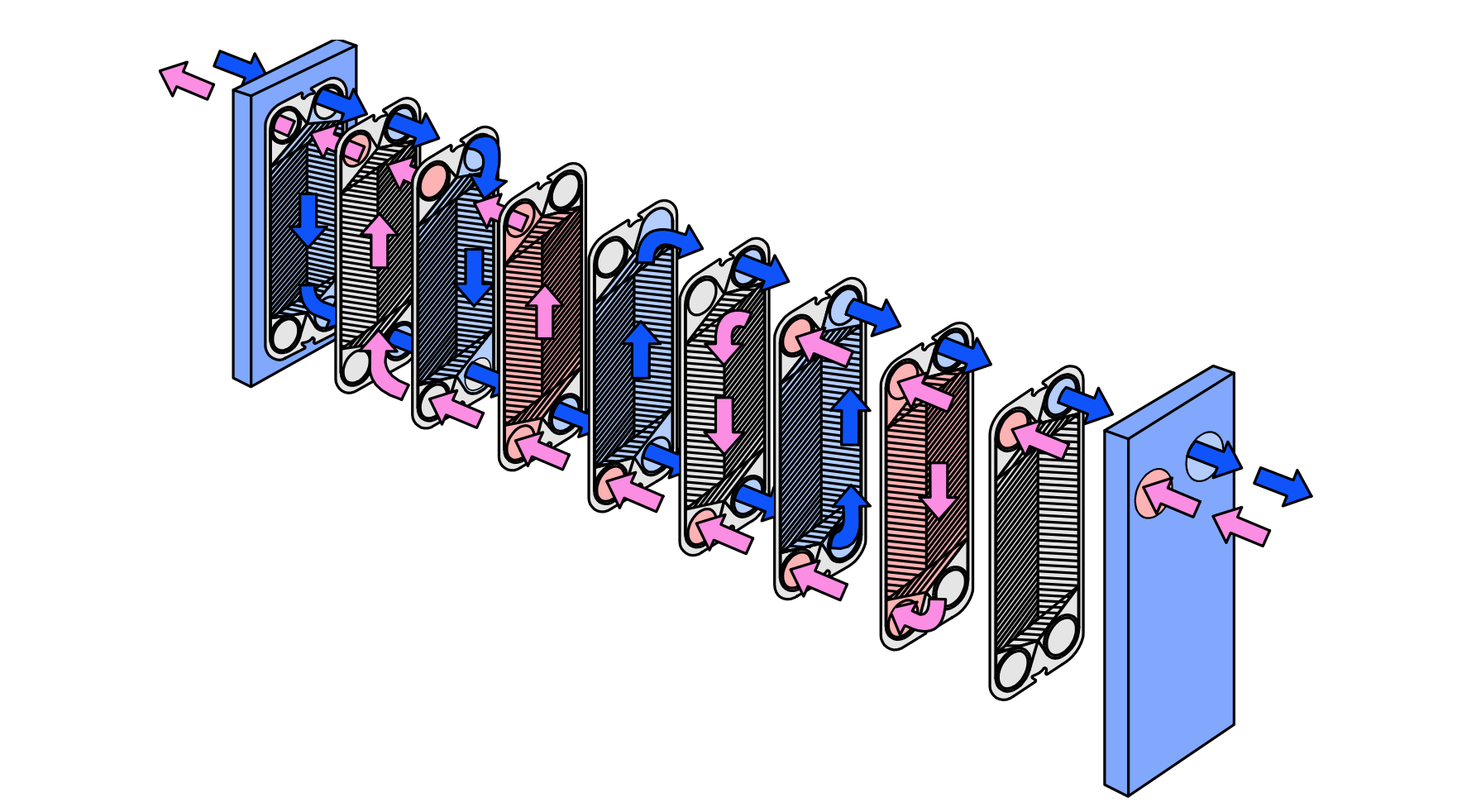
How is a plate heat exchanger made up?
The plates used in a plate and frame heat exchanger are obtained by pressing a single piece of metal. Stainless steel is a metal commonly used for plates due to its ability to bear high temperatures and its resistance to corrosion. Although the use of this material could increase its initial costs, the return on investment is attractive from the durability and maintenance approach.
Semi-welded plates heat exchangers
There are technologies in semi-welded plates heat exchangers ; in these welded channels and channels with traditional joints are alternated. The refrigerant flows in welded channels and the only ones in contact with the refrigerant are two joints between the pairs of welded plates.
These joints are made of resistant materials, joined together to facilitate replacement as their design is glue free. The secondary medium flows in channels sealed by elastomer gaskets with double sealing and corrosion resistant. In this type of design, the materials of the plate prevent the mixing of medium, thereby obtaining the absence of sealing welds that retain the pressure and a flexible design but it is resistant to vibrations.
Corrugated plates heat exchangers.
The concept of plate heat exchanger with flow channels formed by corrugated plates and the heat transfer that is carried out through the thin plates, is currently one of the heat exchange methods with the highest technical efficiency.
The turbulent flow, together with low pollution factors and high heat transfer coefficients, results in the possibility of operating with a small temperature difference in the cooling water and evaporation. This provides good results in the operation and high values of COP (Coefficient of performance).
It also means that a semi-welded plate heat exchanger becomes much more compact than a shell and tube heat exchanger for the same purpose.
What are the applications of these heat exchangers?
Plate heat exchangers are ideal for applications where the fluids have a relatively low viscosity and do not contain particles. In addition, they are ideal when the output temperature of the product and the entry temperature of the service are very similar.![]()
Uses of plate exchangers
Due to its characteristics, this type of exchangers are highly recommended for:
- For industrial use such as Pharmaceutical, Food, Chemical, Petrochemical, Power Plants, Steel Plants, Marine and others.
- Dry cooling towers.
- Water heaters and other fluids, through steam.
- Oil Coolers
- Heat recovery, particularly with short temperature differentials.
- Management of corrosive substances, medium.
- Salt water coolers.
- For any application where short temperature differentials are required.
- For the usage of freezing free refrigeration.
Uses of compact exchangers of welded plates
This type of exchangers can be used for refrigeration purposes in:
- Evaporators,
- Condensers,
- Subcooler,
- Desuperheaters,
- Cascade / Capacitor Evaporators.
Or for processes such as:
- Steam heaters
- Steam condenser
- Liquid Nitrogen Coolers
- Hydraulic Oil Coolers, etc.
What are the advantages of these heat exchangers?
The practical advantages are:
- Less weight
- Smaller space requirements
- Less volume when refilling the system with refrigerant
This type of equipment is not sensitive to temperature shocks, and there is no vibration due to the small distance between support points. There is no pressure retaining the welds of it. Due to the turbulent flow, the risks of freezing are small, as the design will accommodate the expansion avoiding damage if freezing occurs.
Related
Discover more related articles

Basic cooling equipment for the Hospitality Industry
The hospitality industry is generating serious challenges and business opportunities for the refrigeration industry the world over. It spans through...
Read more »
Why choosing Froztec as your refrigeration support?
Any industrial refrigeration project requires engineering support that takes into account all the calculations and tech requirements to ensure its...
Read more »
